Stress Concentration Factors
This page provides a set of interactive plots for common stress concentration factors. See the reference section for more details.
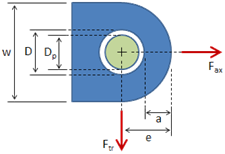
Rectangular Bar With Central Hole, Axial Force
This tab defines the stress concentration factor for a bar with a rectangular cross section and a central circular hole. The bar has an applied axial force (tensile or compressive).
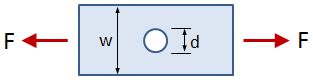
- w = bar width
- d = hole diameter
- t = bar thickness
- F = applied force (tensile or compressive)
The maximum stress is calculated as σmax = Kt σnom, where Kt is the stress concentration factor as determined from the plot below, and σnom is calculated as:
Input Geometry:
Results:
d/w:
Kt:
The value of the stress concentration factor is calculated by:
Sources:
Rectangular Bar With Central Hole, Out-of-Plane Bending
This tab defines the stress concentration factor for a bar with a rectangular cross section and a central circular hole. The bar has an applied out-of-plane bending moment.
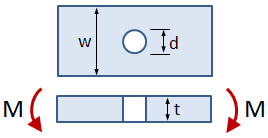
- w = bar width
- d = hole diameter
- t = bar thickness
- M = applied bending moment
The maximum stress is calculated as σmax = Kt σnom, where Kt is the stress concentration factor as determined from the plot below, and σnom is calculated as:
Input Geometry:
Results:
d/t:
d/w:
Kt:
The value of the stress concentration factor is calculated by:
Sources:
Rectangular Bar With U-Notches, Axial Force
This tab defines the stress concentration factor for a bar with a rectangular cross section and two U-notches. The bar has an applied axial force (tensile or compressive).
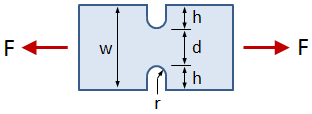
- w = bar width
- h = notch height
- r = notch radius
- t = bar thickness
- F = applied force (tensile or compressive)
The maximum stress is calculated as σmax = Kt σnom, where Kt is the stress concentration factor as determined from the plot below, and σnom is calculated as:
Input Geometry:
Results:
d:
w/d:
r/d:
h/r:
Kt:
The value of the stress concentration factor is calculated by:
where the coefficients in the equation above are calculated from "Peterson's Stress Concentration Factors":
| 0.1 ≤ h/r ≤ 2.0 | 2.0 ≤ h/r ≤ 50.0 | |
|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.955 + 2.169 √h/r − 0.081 (h/r) | 1.037 + 1.991 √h/r + 0.002 (h/r) |
| C2 | −1.557 − 4.046 √h/r + 1.032 (h/r) | −1.886 − 2.181 √h/r − 0.048 (h/r) |
| C3 | 4.013 + 0.424 √h/r − 0.748 (h/r) | 0.649 + 1.086 √h/r + 0.142 (h/r) |
| C4 | −2.461 + 1.538 √h/r − 0.236 (h/r) | 1.218 − 0.922 √h/r − 0.086 (h/r) |
Sources:
Rectangular Bar With U-Notches, Bending
This tab defines the stress concentration factor for a bar with a rectangular cross section and two U-notches. The bar has an applied in-plane bending moment.
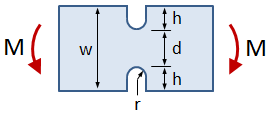
- w = bar width
- h = notch height
- r = notch radius
- t = bar thickness
- M = applied bending moment
The maximum stress is calculated as σmax = Kt σnom, where Kt is the stress concentration factor as determined from the plot below, and σnom is calculated as:
Input Geometry:
Results:
d:
w/d:
r/d:
h/r:
Kt:
The value of the stress concentration factor is calculated by:
where the coefficients in the equation above are calculated from "Peterson's Stress Concentration Factors":
| 0.1 ≤ h/r ≤ 2.0 | 2.0 ≤ h/r ≤ 50.0 | |
|---|---|---|
| C1 | 1.024 + 2.092 √h/r − 0.051 (h/r) | 1.113 + 1.957 √h/r |
| C2 | −0.630 − 7.194 √h/r + 1.288 (h/r) | −2.579 − 4.017 √h/r − 0.013 (h/r) |
| C3 | 2.117 + 8.574 √h/r − 2.160 (h/r) | 4.100 + 3.922 √h/r + 0.083 (h/r) |
| C4 | −1.420 − 3.494 √h/r + 0.932 (h/r) | −1.528 − 1.893 √h/r − 0.066 (h/r) |
Sources:
Rectangular Bar With Fillet, Axial Force
This tab defines the stress concentration factor for a bar with a rectangular cross section and a fillet. The bar has an applied axial force (tensile or compressive).
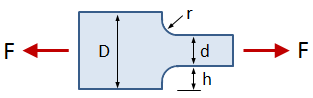
- D = width of larger section
- d = width of smaller section
- r = radius of fillet
- t = bar thickness
- F = applied force (tensile or compressive)
The maximum stress is calculated as σmax = Kt σnom, where Kt is the stress concentration factor as determined from the plot below, and σnom is calculated as:
Input Geometry:
Results:
h:
r/d:
D/d:
h/r:
Kt:
The value of the stress concentration factor is calculated by:
where the coefficients in the equation above are calculated from "Roark's Formulas for Stress and Strain":
| 0.1 ≤ h/r ≤ 2.0 | 2.0 ≤ h/r ≤ 20.0 | |
|---|---|---|
| C1 | 1.007 + 1.000 √h/r − 0.031 (h/r) | 1.042 + 0.982 √h/r − 0.036 (h/r) |
| C2 | −0.114 − 0.585 √h/r + 0.314 (h/r) | −0.074 − 0.156 √h/r − 0.010 (h/r) |
| C3 | 0.241 − 0.992 √h/r − 0.271 (h/r) | −3.418 + 1.220 √h/r − 0.005 (h/r) |
| C4 | −0.134 + 0.577 √h/r − 0.012 (h/r) | 3.450 − 2.046 √h/r + 0.051 (h/r) |
Sources:
Rectangular Bar With Fillet, Bending
This tab defines the stress concentration factor for a bar with a rectangular cross section and a fillet. The bar has an applied in-plane bending moment.
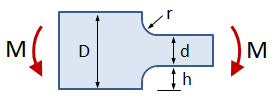
- D = width of larger section
- d = width of smaller section
- r = radius of fillet
- t = bar thickness
- M = applied bending moment
The maximum stress is calculated as σmax = Kt σnom, where Kt is the stress concentration factor as determined from the plot below, and σnom is calculated as:
Input Geometry:
Results:
h:
r/d:
D/d:
h/r:
Kt:
The value of the stress concentration factor is calculated by:
where the coefficients in the equation above are calculated from "Roark's Formulas for Stress and Strain":
| 0.1 ≤ h/r ≤ 2.0 | 2.0 ≤ h/r ≤ 20.0 | |
|---|---|---|
| C1 | 1.007 + 1.000 √h/r − 0.031 (h/r) | 1.042 + 0.982 √h/r − 0.036 (h/r) |
| C2 | −0.270 − 2.404 √h/r + 0.749 (h/r) | −3.599 + 1.619 √h/r − 0.431 (h/r) |
| C3 | 0.677 + 1.133 √h/r − 0.904 (h/r) | 6.084 − 5.607 √h/r + 1.158 (h/r) |
| C4 | −0.414 + 0.271 √h/r + 0.186 (h/r) | −2.527 + 3.006 √h/r − 0.691 (h/r) |
Sources:
Need More Functionality?
Sign up for an account to receive full access to all calculators and other content. The subscription types are described below, along with the benefits of each.
- Price
- Access to Calculators
- Login
- Create Materials
- Create Cross Sections
- Save Files
- Reporting
- Free
-
LimitedLimited Access to Calculators
-
NoneNo Login
-
Pre-defined Materials
-
Pre-defined Cross Sections
-
No Saved Files
-
No Reporting
- Learn More »
-
USD $9.99 /month USD $99.99 /year -
FullFull Access to Calculators
-
IndividualIndividual Login
-
Create Materials
-
Create Cross Sections
-
Unlimited Saved Files
-
Unlimited Reporting
- Learn More »
- Sign Up Now
-
USD $29.99 /month USD $299.99 /year -
FullFull Access to Calculators
-
Floating LicensesFloating Licenses
-
Create Materials
-
Create Cross Sections
-
Unlimited Saved Files
-
Unlimited Reporting
- Learn More »
- Sign Up Now
-
Bulk pricing (≥20 educational licenses)
-
FullFull Access to Calculators
-
Floating LicensesFloating Licenses
-
Create Materials
-
Create Cross Sections
-
Unlimited Saved Files
-
Unlimited Reporting
- Learn More »
- Sign Up Now
Looking for Other Calculators?
Here are just a few of the calculators that we have to offer:
Feedback
Do you have any comments or suggestions? We would love to hear them!