Column Buckling Validation
This section details the validation for the Column Buckling calculator. Several examples are worked through to determine expected results such as critical stress, critical force, and critical length. These expected results are then compared to the actual output of the Column Buckling calculator.
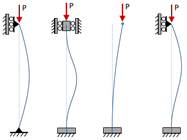
Case 2: Central Load, Fixed-Free
In this validation, a column with the following properties will be analyzed:
| Applied Compressive Load, F: | 5000 lbf |
| Material: |
6061-T6 Aluminum Yield Strength, Sty = 35,000 psi Elastic Modulus, E = 10e6 psi |
| Cross Section: |
Circle, 1 inch diameter Area, A = 0.7854 in2 Centroidal Distance, c = 0.5 in Radius of Gyration, r = 0.25 in |
| Length (unsupported), L: | 6 in |
| Eccentricity: | None |
| End Condition: | Fixed-Free (K = 2.1) |
Manual Calculations
The slenderness ratio of this column is:
$$ R_s = {L \over r} = {6 \text{ in} \over 0.25 \text{ in}} = 24.0 $$Since the force is applied centrally (along the column axis), the critical stress will be determined by either the Euler formula (if the column is long) or the Johnson formula (if the column is intermediate). The transition ratio should be calculated to determine whether the column is long or intermediate:
$$ R_{trans} = \sqrt{ {2 \pi^2 E \over K^2 S_{ty} } } = \sqrt{ {2 \pi^2 (10e6 \text{ psi}) \over 2.1^2 (35000 \text{ psi}) } } = 35.76 $$The transition length corresponding to the transition ratio above is:
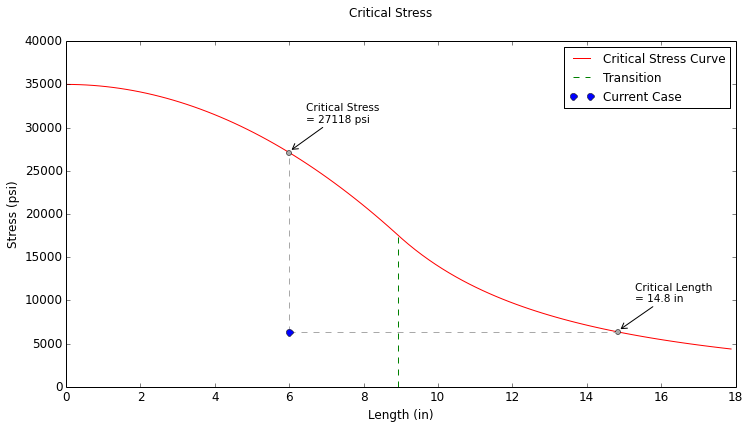
$$ L_{trans} = R_{trans}r = (35.76)(0.25 \text{ in}) = 8.94 \text{ in} $$Since the slenderness ratio of the column is less than the transition ratio (and likewise, the length of the column is less than the transition length), this column is considered intermediate. Therefore, the Johnson formula will be used to determine the critical stress:
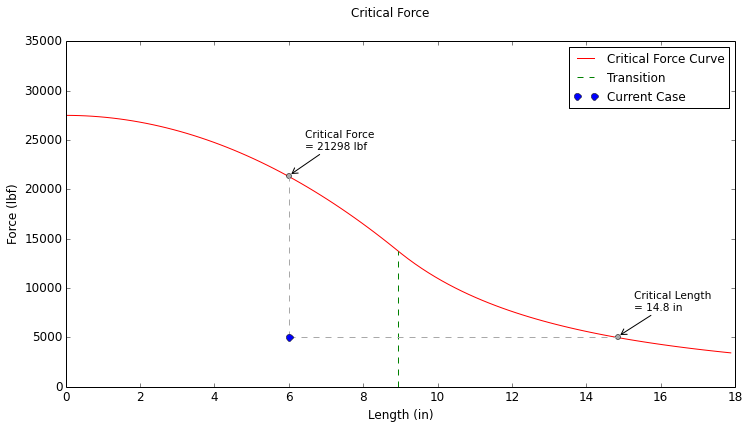
The critical force corresponding to the critical stress above is:
$$ F_{cr} = \sigma_{cr} A = (27118 \text{ psi})(0.7854 \text{ in}^2) = 21,298 \text{ lbf} $$The critical length is found by iterating the column length until the critical force equals the applied force. We will initially assume that the critical length value would put the column into the "long" regime, so the Euler formula will be used during the iteration. At an unsupported length of \(14.82\) inches, the critical force of the column, per the Euler formula, is:
$$ F_{cr} = { \pi^2 EA \over \left( K {L \over r} \right) ^2 } = { \pi^2 (10e6 \text{ psi})(0.7854 \text{ in}^2) \over \left( 2.1 {14.82 \text{ in} \over 0.25 \text{ in}} \right) ^2 } = 5,002 \text{ lbf} $$The slenderness ratio of a column with a length of 14.82 inches is:
$$ R_s = {L \over r} = {14.82 \text{ in} \over 0.25 \text{ in}} = 59.28 $$Since the slenderness ratio of \(59.28\) is greater than the calculated transition ratio of \(35.76\), the assumption of a long column when calculating the critical length was correct.
In summary:
| Critical Stress: | \( 27,118 \text{ psi} \) |
| Critical Force: | \( 21,298 \text{ lbf} \) |
| Critical Length: | \( 14.82 \text{ in} \) |
Comparison With Calculator
The Critical Stress Plot for this case is shown below. From this plot it can be seen that the critical stress and the critical length match the values that were calculated above.
The Critical Force Plot for this case is shown below. From this plot it can be seen that the critical force and the critical length match the values that were calculated above.